
Companies with a customer
experience mindset drive a higher revenue than the rest of their
industries. Companies known for leadership in customer
experience tend to stand out from the competition and to
outperform competitors remarkably.
Building an effective customer experience practice requires a
holistic approach. To take a holistic approach to customer
experience, you must consider the entire customer journey,
across all channels and over time.
3 Keys to Improving Customer Experience
Consider the Entire Customer Journey. Empathize with your
customers and analyze the experience from their point of view.
When and how do they interact with your brand, products,
services, or people? Create a separate customer experience
practice, a team of independent associates who can view the
overall customer experience in a more unbiased manner.
Involve Everyone. Engagement in building an effective customer
experience must be an active pursuit at all levels in ways that
are relevant for them. The relationship between customer
experience and revenue trends can shine a light on the actual
customer experience and help executives to develop more
effective customer-focused strategies.
Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration. Roll out tools,
processes, and programs and processes that facilitate
cross-functional collaboration led by CX champions. Play
simulation games, like INNOBALL, with most promising ideas.
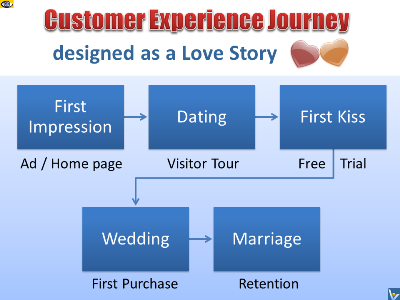
Customer Experience Journey
Customer experience (CX) is your customers' holistic perception
of their experience with your business or brand during all
stages of the consumption process including pre-purchase,
consumption, and post-purchase stages.
The interactions and experiences your customers have with your
business define its success or failure. Great customer
experience throughout the entire customer journey, from the
first contact through outstanding after-sale service turns a
first-time buyer to a happy and loyal customer.
For a brand, it is extremely important to make a great first
impression on a customer because this impression lasts and
influences all future encounters.
The next step is to win trust of a potential customer. This can
be done through visitor tours, testimonials, success stories,
empathy and white marketing.
A free trial of a product or service helps to engage a potential
customer. It is also a key element of experiential marketing.
The first sale is like a wedding. It is the first step to
creating a loyal customer. Find way to make the event enjoyable
and memorable for the customer
Today, customer loyalty is driven primarily by a company's
interaction with its customers, how well it delivers on their
needs and wants, and how often the company exceeds customers’
expectations. A company's ability to deliver a customer
experience that sets it apart in the customers’ eyes will
increase the amount of consumer spending with the company and
inspire loyalty to its brand.
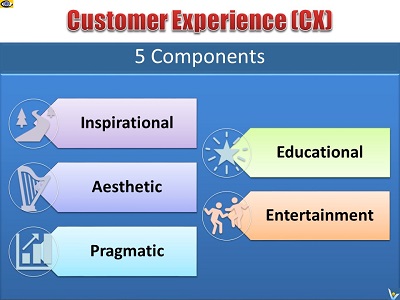
Five Components of Customer
Experience
Five parts of customer experience include inspirational,
aesthetic, pragmatic, educational, and entertainment,
components.
1.Inspirational. Create amazing innovative customer value and
give your customers that stretches their aspirations and exceeds
their expectations. If you create a radically innovative
product/service, focus on enthusiast customers and inspire them
by radically new opportunities your product creates.
2. Aesthetic. Customer experience should give great aesthetic
pleasure. Aesthetic means the pleasant, positive or artful
appearance of a person or a thing. It is about how something
looks and feels, and concerned with beauty or the appreciation
of beauty. You must understand the nature of a beautiful
experience as it is perceived by a customer, master the art of
creation of that beauty and the art of communication and
delivery of a beautiful customer experience so it get
appreciated by your customer.
3. Pragmatic. Pragmatic experience is about how a customer feels
about the cost/benefits ratio of a product or service.
4. Educational. People love to learn new useful things and grow
through learning. Educate your customers, but do it in an easy,
eye-opening and joyful way. Education should be fun for your
customers.
5. Entertainment. People love to be entertained. Add humor to
your customer relationship. Keep engaging customers with various
fun activities.
Towards Greater Customer
Experience
Customer experience management (CXM) is the process that
companies use to oversee, track and improve all interactions
with a customer during the entire customer journey. This
involves co-creation of value innovations in partnership with
customers, creation of a powerful first impression, empathetic
marketing, selling outstanding benefits and solutions to
customer problems, building harmonious customer relationship,
win-win approach to resolving conflicts, and exceeding customer
expectations.
Although most businesses state that they offer a "great customer
experience," this contrasts with most customers expressing
dissatisfaction with their experience. To meet the demands of
providing an exceptional customer experience, companies must be
able understand customers’ perception of value and deliver it
consistently.
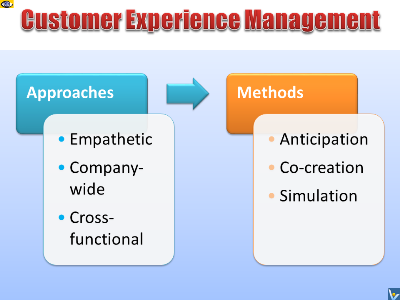
Holistic Cross-functional Approach
Building great customer experience requires a holistic
cross-functional approach, involving CEO commitment, business
design, brand appeal, customer-focused value-creation culture,
entrepreneurial strategies, integration of technology and
continuous company-wide effort. Recognize CXM as the future of
marketing, sales and customer service. Use this approach to
adopt the mindset of the customer and anticipate customer needs.
Play simulations games, like INNOBALL, with emerging challenges
and opportunities not just to make a project more successful,
but also to turn anticipation of new customer needs and creation
customer-focused innovations into a winning habit.
Optimizing Customer Experience
The aim of Customer Experience Management (CXM) is to ensure
that customers are completely satisfied – or more than satisfied
– in order to gain their loyalty and to turn them to repeat
customers and brand ambassadors.
The interest in CXM is increasing because businesses are looking
for competitive differentiation.[
To ensure CXM accuracy and to make the best use of it, the
customer journey must be viewed from the actual perspective of
customers, not the seller.
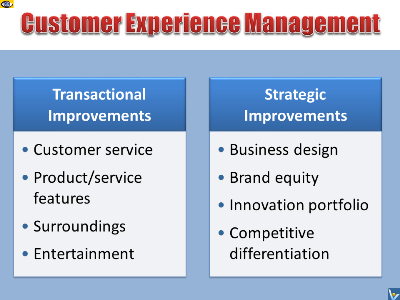
Two CXM Levels: Strategic and Transactional
At the strategic level, CXM depicts a business strategy designed
to manage the customer experience, to give strategic benefits to
both sellers and customers, and to increase the firm’s brand
equity.
At the transactional level, CXM can be monitored through
customer feedback, surveys, targeted studies, or observational
studies. It captures responses of customers to their encounters
with the brand or company that can be used to quantify the cost
of inaction on customer experience issues.
Brand Ambassadors
The role of a word of mouth form of marketing grew exponentially
due to exponential growth of social media. You must amaze your
existing customer and exceed their expectations to turn them to
your ‘evangelists’ – people who talk about their customer
experience with great enthusiasm.
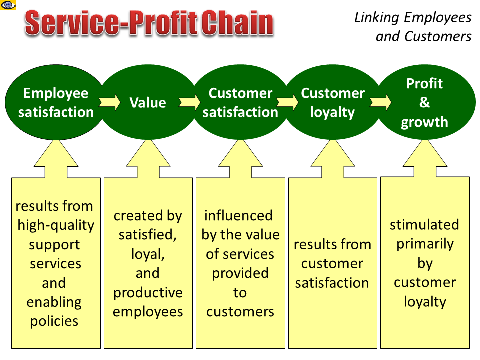
Holistic Approach
The service-profit chain is a powerful phenomenon that stresses
the importance of people – both employees and customers – and
how linking them can leverage corporate performance.
The service-profit chain is an equation that establishes the
relationship between corporate policies, employee satisfaction,
value creation, customer loyalty, and profitability. Unleashing
the power of the service-profit chain will improve your
performance. Moving from a focus on transactions to a focus on
customer relationships delivers sustainable financial
advantages. Your must look beyond the arithmetic value of
individual transactions to all the ways you can serve the
customer to capture and develop lasting relationships.
A seamless integration of all components in the service-profit
chain – employee satisfaction, value creation, customer
satisfaction, customer loyalty, and profit and growth – links
all the critical dynamics of top customer service. The company
guides, nurtures, and empowers its employees, and the employees
play a vital role in securing customer satisfaction and the
benefits that accrue from it.
The Power of Satisfied Employees
Among the factors that motivate employees in the workplace, job
satisfaction is at or near the top of the list, far surpassing
pay and benefits. Creating a work environment that encourages
rapid response to customers' needs and attentive follow-through
is the key to leveraging the power of your service-profit chain.
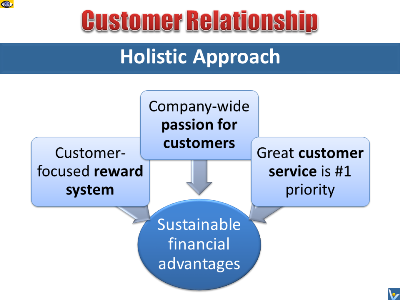
Holistic Approach to Customer
Relationships: 7 Tips
As opposed to a transactional focus, a holistic approach to
customer relationship delivers sustainable financial advantages.
To achieve this:
Be passionate about your customers. Treat customer relationships
as enjoyable win-win interactions of platonic lovers.
Demonstrate continuously that in your company's order of
priorities, customer service comes before all else.
Don't focus solely on transactions. Look beyond the arithmetic
value of individual transactions to all the ways you can serve
the customer to capture and develop lasting mutually beneficial
relationships.
Keep in mind that it is customer, not you, who owns the
relationship. Once you have captured customer relationships,
service the customer relentlessly and keep creating amazing
value innovations.
Understand what motivates your employees in order to develop
powerful tool for dealing with them to get them achieve
extraordinary results. Satisfied employees make a deeper
commitment to the business, make improvement suggestions, and
work harder to satisfy the customer.
Develop financial system that truly captures the financial
dynamics of customer relationships.
Develop system that rewards people for building and maintaining
strong and lasting customer relationships.
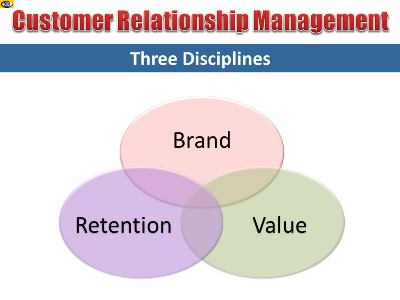
Brand Equity
Brand equity refers to the customers’ subjective appraisal of
the brand. There are many ways to measure your brand appeal and
brand equity. You can measure it at the firm level, at the
product level, or at the consumer level. The consumer level
approach seeks to map the mind of the customers to find out what
associations with the brand they have. Brands with higher levels
of awareness and strong, favorable and unique associations have
higher brand equity.
Customer Value Analysis
Value equity refers to the customers’ perceptions of value.
Value and quality are all about customers’ perceptions. Like
beauty and truth, quality is in the eye of the beholder.
"Perception is all there is..." says Tom Peters. "There is only
one perceived reality, the way each of us chooses to perceive a
communication, the value of a service, the value of a particular
product feature, the quality of a product.“ From the customer’s
point of view, your customer relationship management efforts
create additional value if they improve your responsiveness,
reduce prices, and make customer’s life more enjoyable. To
create greater value, Imagine the ideal customer experience and
strive to provide it.
Customer Loyalty Analysis
Retention equity refers to the firm building relationships with
customers and encouraging repeat-purchasing. Customer loyalty is
a major contributor to sustainable profit growth. To win
customer loyalty, you must first satisfy your customer
repeatedly.
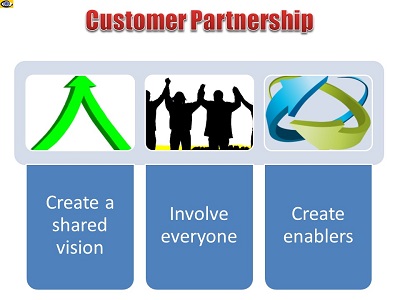
Create a Shared Future
Customer satisfaction and retention are critical to success any
business. You must partner with your customers and to create a
shared future that is more secure than either could have built
alone. Ask your major customers what they are planning to
achieve, inform them about your strategic intent, formulate a
shared vision, and then discuss how you could make the desired
future a reality jointly.
Involve Everyone
Create a customer-focused culture, get employees passionate
about customer, and make customer partnership everybody’s job.
Leaving establishment of customer partnership to isolated
departments like sales or customer service is a mistake.
Everybody in your company, from front-line employees to top
managers, must find ways to connect with customers in a mutually
beneficial way. Your business exists to serve its customers, and
this recognition should permeate every strategy, process,
department, project, and job role.
Partner with all types of customers – not just existing ones,
but also potential and lost customers. Existing customers may
help you improve your customer services and create innovative
customer value. Potential customer may help you understand why
they aren't buying your product or services and what could turn
them to buyers. Lessons learnt from lost customer can prevent
future losses.
Create Enablers
Create platforms and mechanisms that will make it easier for
customers to share their ideas, to discuss matters of mutual
interest, and to collaborate with you.
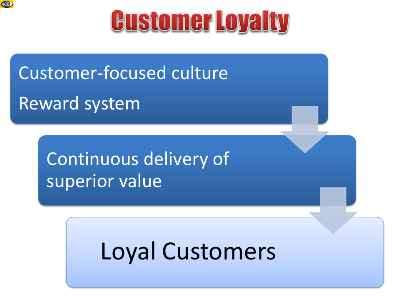
Customer Loyalty: Benefits for
Business
Delighted and loyal customers will return for follow-on business
without considering alternatives of comparing the competition.
Though, there is a number of factors that influence customers'
decisions to remain loyal, true loyalty is based on your
company's continuous delivery of superior value. Customer
loyalty is a major contributor to sustainable profit growth.
Difference Between Satisfied and Loyal Customers
In highly competitive markets, there is a big difference between
satisfied customers and completely satisfied – or loyal –
customers. The former, if they have a choice, can easily switch
to another supplier, while loyal customer would stay longer with
your company and recommend its services to others. Thus you
should rather be concerned than pleased if, according to your
surveys, majority of your customers fall into the satisfied
category.
How To Win Customer Loyalty
To win customer loyalty, you must first satisfy your customer
repeatedly. According to 80/20 Principle, loyal customers – the
top 20% of total customers – usually account for more than 80%
of your sales and profit growth. Turning customers into loyal
ones through building customer relationship and delivering
superior value should be your prime task. Develop a system for
collecting customer loyalty data and relaying this information
to those responsible for customer value creation. Develop a
reward system that inspires employees to win customer loyalty.
Stakeholder-focused Management
A great business inspires employees by amazing opportunities and
customers by exciting products. Management is perpetual creation
of outstanding value for all stakeholders: customers, employees,
investors and the society. Customer value and buying decisions
are the starting point for the actual practice of management,
its policy and strategy.
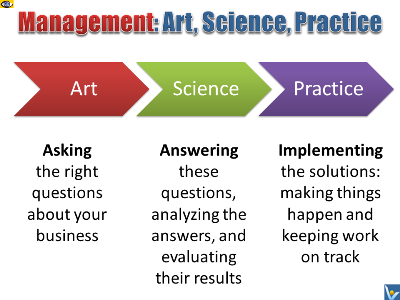
Management is more art than science
Managing is working with and through other people to accomplish
the objectives of both the organization and its members.
Management consists of:
rational assessment of a situation and the systematic selection
of goals and purposes (what is to be done);
systematic development of strategies to achieve these goals;
marshalling of the required resources;
rational design, organization, direction, and control of the
activities required to attain the selected purposes;
helping each employee to find the right fit, directing their
ambitions, developing and empowering employees, providing
situational coaching to help employees to grow, and to enhance
their performance and learning ability;
motivating and rewarding of people to do the work.

Managerial Competency
A managerial competency in general is a set of knowledge, skills
and behaviors that allows a manager to perform his duties
efficiently and effectively.
The seven core competencies necessary to be a good manager are
planning and administration competency, managerial leadership
competency, self-management competency, strategic action
competency, communication competency, teamwork competency, and
multicultural competency.
Planning and Administration as well as Motivation and
Communication are traditional managerial tasks.
Managerial leadership is a modern managerial task. To maximize
long-term business success, an executive should strive to be
both a manager and a leader and to synergize their functions.
Strategic action competency includes strategic action planning,
strategic leadership by example, and strategic experimentation
with opportunities.
In today’s era of empowered employees, manager should be not
just a team manager but also a team worker.
Multi-Cultural competence is required to manage cross-cultural
differences, to harness cultural diversity and to succeed in the
globalized marketplace.
Self-management is a traditional managerial competence.
Self-leadership is a new competence necessitated by today’s era
characterized by rapid change.
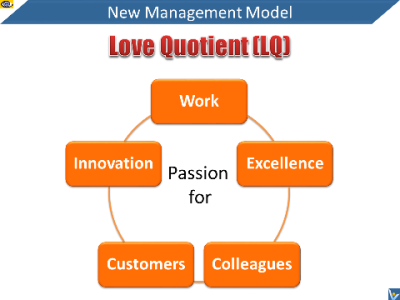
Benefits of High IQ Leadership and
a High LQ Culture
Love quotient (LQ) is your ability to understand, nurture and
express love.
Passion for work, honesty and transparency are the traits of a
high LQ leader who sets an example and creates a high LQ culture
that encourages loving relationships, supports shared values and
inspires positive change. A leader with high LQ has also great
capacity to empathize with and to listen to the concerns that
employees may raise about uncertainties and risks associated
with the changes that are taking place.
The higher the leader’s LQ, the more secure employees feel
because they believe that the changes are coming from a place of
love. Employees feel loved and trusted. They are empowered and
are willing to experiment with new ideas, learn from failures
and start again wiser.
Creating a Desired Future State
High LQ managers empathize with their internal and external
customers. They are open to understanding new trends and the
impact they will have on their markets. Leaders with a high LQ
adopt a customer-centric mindset, focus on meeting the needs of
future customers and create – actively and systematically – a
movement to achieve a future desired state.
High LQ strategists understand the growing role of customer
empowerment and ensure that the firm is focused on developing
solutions that will appeal to next generation customers.
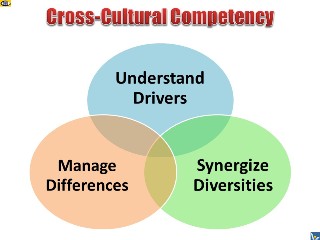
Cross-Cultural Competency as a Key
to Leveraging Diversity
A globally connected world is a key driver of structural change
for the global workforce. Cross-cultural competency is the key
enabling factor of working in diverse teams. The diversity of
stakeholders is also an important point to consider. Employee,
customers, partners, competitors are all made up of people of
different ethnical backgrounds, who have different views,
perceptions, beliefs, and values.
Creativity and Innovation
Innovation became a systemic phenomenon. It is achieved through
synergizing diversities and is increasingly more dependent on
the collaboration between actors from different cultural
backgrounds who combine their own perceptions, thinking habits
and expertise to create something new. This happens on all
levels − individual, team, institutional. Diversity of thought
increases creativity and, with it, the innovation potential of
individuals, teams, corporations and joint ventures.
International Business
Business activities that take place abroad emphasize the
importance of cultural intelligence and effective cross-cultural
communication between the business and local people. Unless
company representatives have good understanding of the local
traditions and values, they might behave in such a way that is
considered offensive or inappropriate in another culture and
facilitate conflict, putting the whole local business at risk.
In order to effectively perform business activities in a
different cultural setting, company representatives must possess
such soft skills, as sociocultural competence and empathy.
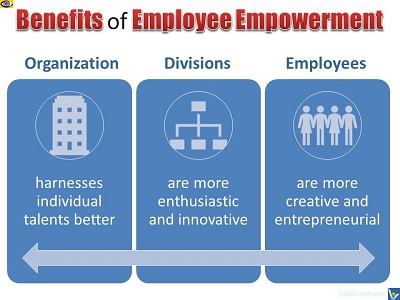
Benefits of Employee Empowerment
In losing organizations, people are the most underutilized
resource. In winning organizations, thanks to employee
empowerment:
The organization harnesses individual talents to the full;
employee empowerment changes the managers' mind-set and leaves
them with more time to engage in broad-based thinking,
visioning, and nurturing;
The department / team becomes more enthusiastic, active, and
successful; facilitates teamwork and harnessing of collective
power of employees;
Employees are entrusted new responsibilities and are stretched
beyond what they previously thought they could achieve;
empowerment releases the individual wisdom, creativity and
energy of employees.
Empowerment is the oil that lubricates the exercise of learning.
Talented and empowered human capital is becoming the prime
ingredient of organizational success. A critical feature of
successful teams, especially in knowledge-driven enterprises, is
that they are invested with a significant degree of empowerment,
or decision-making authority. Equally important, employee
empowerment leaves managers with more time to work on the
business. This intelligent and productive division of duties
between entrepreneurial leaders, focusing on emerging
opportunities, and empowered employees, running the business
unit day to day (with oversight on the leader's part) provides
for a well-managed enterprise with strong growth potential.
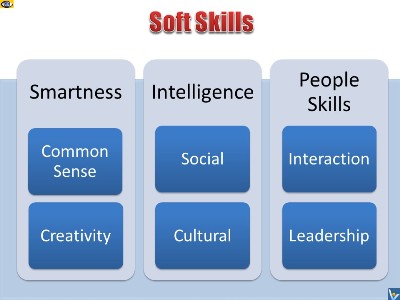
Definition and Importance of Soft
Skills
Soft skills are a synergistic combination of common sense,
creativity, decision making skills, problem solving skills,
empowering attitudes, the ability to make a desired first
impression and to be charismatic, people skills, social skills,
communication skills, the ability to build rapport, the ability
to lead, social intelligence, emotional intelligence, and
cultural intelligence, among others, that enable people to
navigate their environment, work well with others, perform
efficiently, and achieve their goals with complementing hard
skills.
Soft skills are just as important as hard skills because they
are the foundation of planning, cooperation, management,
innovation, marketing, etc. The influence of soft skills on the
outcome of business activities depends on the circumstances in
which the business activity takes place.
In the digital economy where the large majority of the work can
be done by computers, the primary role of human beings is to use
their imagination and creativity to invent new things and to
solve problems in outside-the-box ways.
Soft skills form the basis of successful leadership and are,
therefore, highly important for those in leading positions.
Effective communication inside the company is the foundation of
successful business activities. Communication allows employees
at all levels to coordinate their actions to achieve a common
objective.
Due to the scope and complexity of business operations, top
managers have to rely on their staff to assist them in the
decision-making process.

Breakthrough Soft Skills
Breakthrough soft skills help you to create breakthroughs:
stretch yourself, be aa thought leader, initiate radical value
innovations and excite and enthuse others to join your crusade,
create disruptive innovations jointly with others, lead
transformational change and radical projects.
Examples of breakthrough soft skills include awakening the inner
genius, disruptive thinking, strategic creativity, subconscious
ideation, serendipity, venturepreneurial inspirational
leadership, intrapreneurship, spotting and pursuing
opportunities, venturepreneurial simulation, risk taking,
anticipation, intuition, synergistic teamwork, creative
marketing and selling of radically new ideas and solutions, and
creating new customers desires.
Advanced Soft Skills
Advanced soft skills help you achieve above average results and
create evolutionary innovations.
Examples of advanced soft skills include creative
dissatisfaction, self-leadership and self-coaching, lateral
leadership and leading-up, love quotient, spoken innovation,
attitude motivation, being a creative team worker, intellectual
cross-pollination, mutual creativity, making presentations that
inspire change, knowing how to win wisely, and how to conquer a
stronger opponent.
Lifestyle Soft Skills
Lifestyle soft skills are general thinking, social and people
skills